CRM Sales Pipeline Management
- What factors do you need to consider to select the right CRM process?
- What is meant by CRM, as the term is traditionally used?
- Get your own fully customizable CRM now - click here to get it
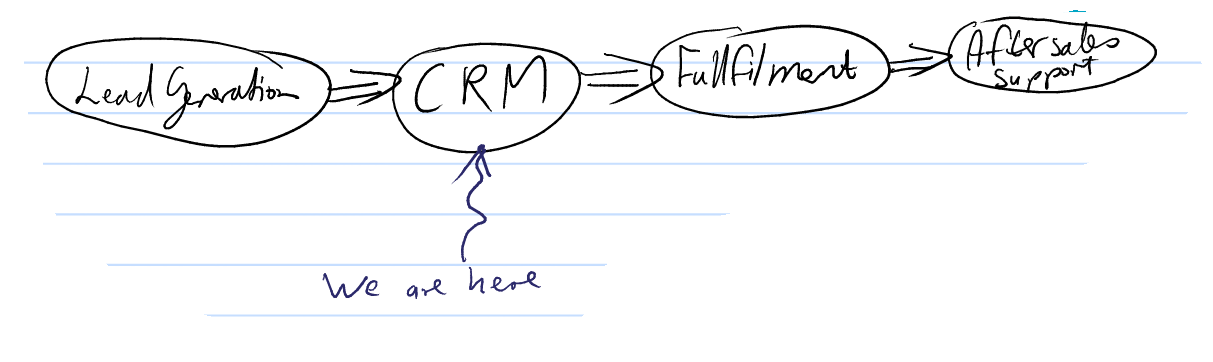
Where does CRM fit into your overall business process?
Learn more
Lead Generation
Your lead generation is your marketing efforts, the methods by which you intend to fill your sales funnel.
This may consist of inbound calls, lead capture forms on the web, direct reponse marketing, inbound marketing phone numbers, or outbound canvassing whether to cold leads, databases, or warm prospecting efforts from your sales staff themselves.
If this is an activity performed by your sales staff, you may consider adding it as a step on the front of your CRM process, otherwise it falls outside the process boundary for CRM.
CRM: The process that converts sales opportunities into closed deals.
Who interacts with this process - 3 perspectives
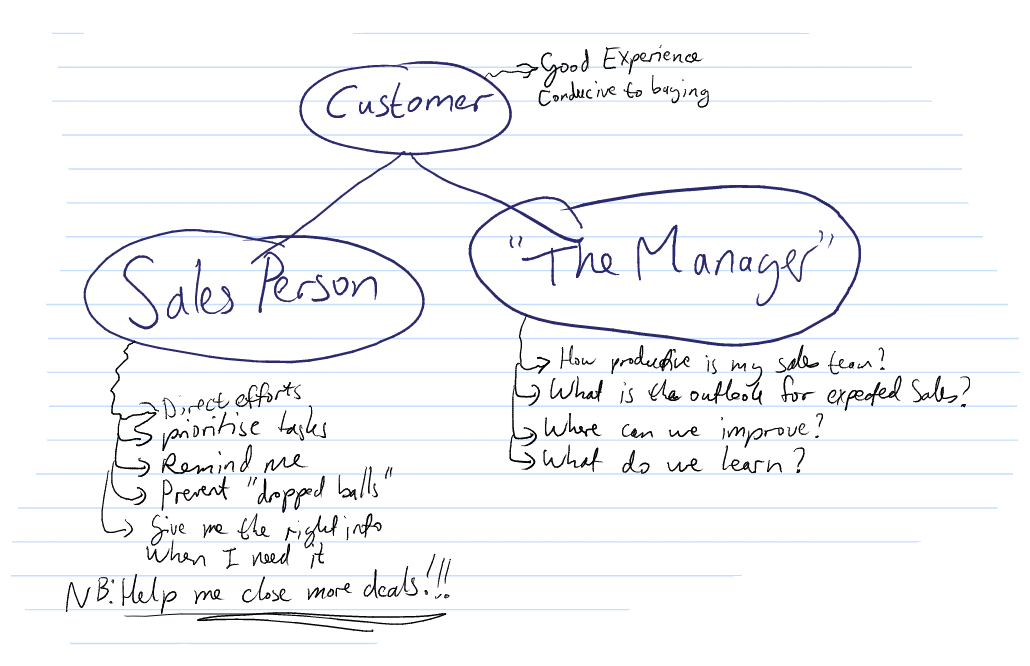
- The Customer should be the core consideration for designing your CRM process. Customers must have a good experience that is conducive to creating a "buying" state.
- The Sales Person is the primary user of the CRM, and the system should be as user friendly and inviting to the sales person to use as is possible.
The CRM sould help the sales person:
- Prioritise actions
- Keep track of activities and reminders about follow ups and next steps
- Provide the right information at the fingertips of the sales staff when they need it
- Prevent "dropped balles"
- Help the sales person maximise sales
- The Company perspective or "The Manager" needs
- easy transparency and visibility over the sales funnel
- determine the productivity and performance of the sales team
- gain intelligence and understanding about how to further improve results
How to design the right CRM process for your organisation
You probably don't have a strong need for CRM when:(a) Customers make their decision to purchase with relatively little input from sales staff.
(b) The average transaction value or margin is low.
(c) The opportunity for repeat sales is low, or the value there-off is too low to justify special efforts.
Points to consider:
- Should you segment your sales funnel by target customer segments - do some segments warrant more attention or a different sales funnel with different steps in it?
- Where is the greatest value to be gained by increasing the throughput rate of prospects that can be processed per sales person per month?
- You can only improve what you measure and to control and direct sales efforts you need accurate and detailed metrics that cut into the process
- Type of business can shape the structure of the sales funnel
- An e-commerce business where large parts of the sales funnel needs to be automated
- A retailer where customer demand is driven by physical proximity, price and promotional strategies
- A wholesaler who deals with relatively fixed base of customers placing regular orders
- A consulting business that sells large projects to enterprise customers where each project proposal is tailored to individual customer requirements and have correspondingly long sales cycles
Key Measures
- Average cycle time from first engagement to confirmed sale
- Closing rate
- Average deal size and margin
- Total revenue or Profit contribution generated per time period
- Repeat sales and average total customer lifetime value
- Number of sales
